How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Unleash the Potential of Your Rose Garden sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Imagine transforming a simple rose cutting into a flourishing, fragrant rose bush, adding vibrant color and intoxicating perfume to your garden.
This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to embark on this rewarding journey of rose propagation, unlocking the potential of your own rose garden.
Rose propagation from cuttings is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your rose collection. It allows you to create clones of your favorite roses, preserving their unique characteristics and sharing them with friends and family. This method is surprisingly simple and offers a satisfying sense of accomplishment as you witness the transformation of a small cutting into a thriving rose plant.
Introduction: The Allure of Rose Propagation
Rose propagation is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your garden with beautiful blooms. By learning to propagate roses from cuttings, you can create new plants that are genetically identical to your favorites, ensuring the same stunning colors, fragrances, and growth habits.
Compared to buying new plants, propagating roses from cuttings offers several advantages:
Benefits of Rose Propagation
- Cost-Effectiveness:Propagating roses from cuttings is significantly cheaper than purchasing new plants, allowing you to grow a larger collection without breaking the bank.
- Genetic Preservation:Cuttings produce plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant, ensuring you maintain the desired traits of your favorite roses.
- Increased Variety:By propagating roses from cuttings, you can create a diverse collection of roses with unique characteristics and colors.
- Personal Satisfaction:There is immense satisfaction in growing new roses from cuttings, knowing you have nurtured them from the beginning.
Rose Types Suitable for Propagation
Most rose varieties can be propagated from cuttings, but some are easier than others.
- Hybrid Tea Roses:These are known for their large, showy blooms and are generally easy to propagate.
- Floribunda Roses:These roses produce clusters of smaller blooms and are also relatively easy to propagate.
- Grandiflora Roses:These roses combine the large blooms of Hybrid Teas with the prolific flowering of Floribundas and are suitable for propagation.
- Shrub Roses:These roses are known for their bushy growth habit and are often easy to propagate.
- Climbing Roses:While some climbing roses can be propagated from cuttings, others may require grafting for successful propagation.
Selecting the Perfect Cuttings
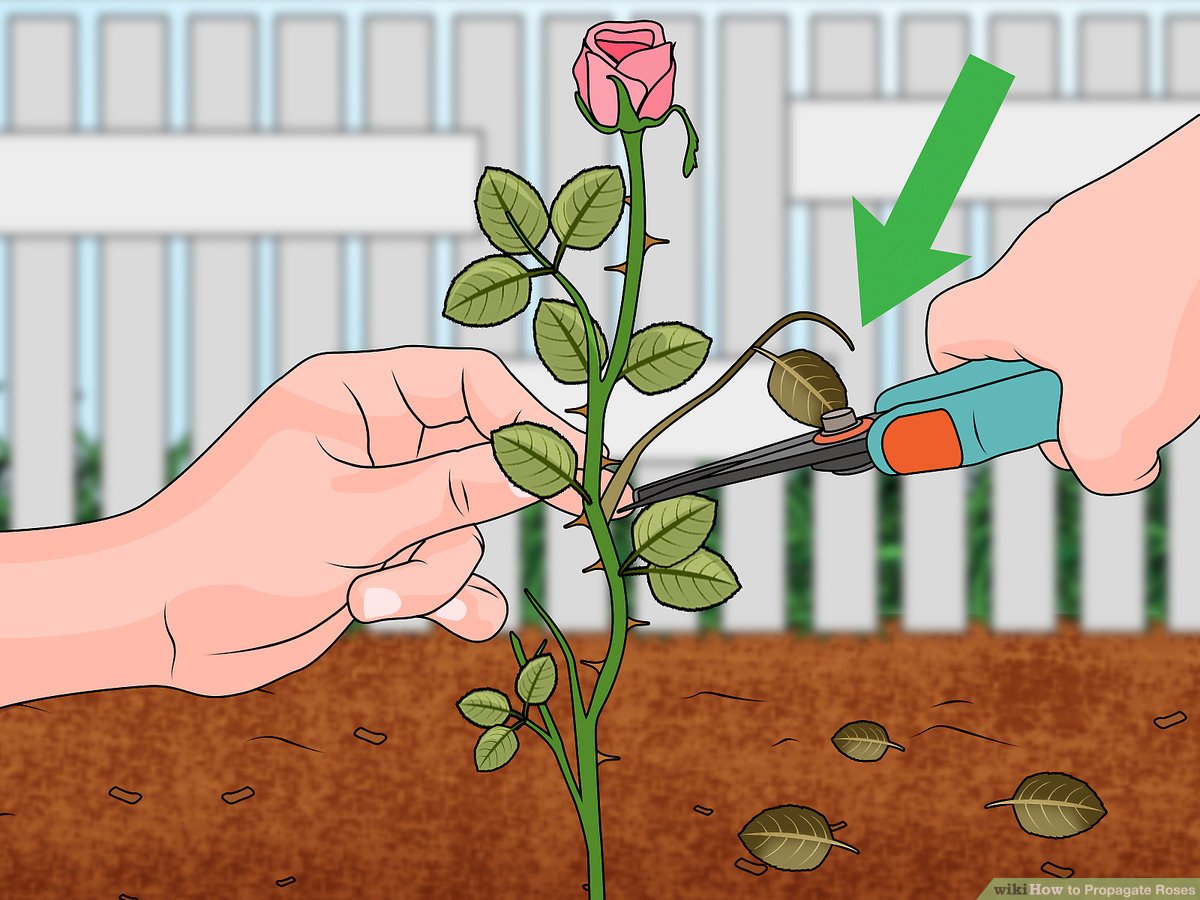
The success of your rose propagation journey hinges on choosing the right cuttings. Selecting healthy, vigorous cuttings from the mother plant ensures a higher chance of successful rooting.
The ideal time to take rose cuttings is during the spring or summer when the plant is actively growing. This is when the stem is most pliable and contains sufficient energy for root development. Avoid taking cuttings during the dormant season (winter) as the plant is conserving energy and may not root as easily.
Choosing Healthy Cuttings
To ensure a successful propagation experience, selecting healthy rose cuttings is crucial. Look for stems that are disease-free, free from insect damage, and exhibit vigorous growth.
- Color:Choose stems that are a vibrant green color, indicating active growth.
- Texture:The stem should feel firm and slightly woody, not soft or mushy. This indicates maturity.
- Nodes:Look for stems with multiple nodes, which are the small bumps along the stem where leaves and roots can develop.
Ideal Cutting Length and Stem Maturity
The length of the cutting is also important for successful rooting. A cutting that is too short may not have enough energy reserves to develop roots, while a cutting that is too long may be difficult to root.
- Length:Aim for cuttings that are 4-6 inches long.
- Stem Maturity:Choose stems that are semi-hardwood, meaning they are not completely soft and pliable but also not completely woody and brittle.
Cutting Preparation
Once you have selected the perfect cuttings, prepare them for rooting by making a clean, angled cut at the bottom of the cutting just below a node. This angled cut helps to increase the surface area for root development.
Preparing the Cuttings for Success

Once you have your cuttings selected, it’s time to prepare them for their journey into becoming new rose bushes. This process involves a few essential steps that will maximize their chances of success.
Making Clean Cuts
Making clean cuts is crucial for successful rose propagation. A sharp, clean cut encourages root development and minimizes the risk of disease.
- Use a sharp knife or pruning shears to make a clean, angled cut just below a node (the point where a leaf grows from the stem).
- An angled cut increases the surface area for root development, while a clean cut prevents the entry of harmful bacteria and fungi.
Removing Leaves from the Lower Portion of the Cutting
Removing leaves from the lower portion of the cutting is essential to prevent them from rotting and consuming valuable energy that should be directed towards root development.
- Remove all leaves below the soil line, as these leaves will be submerged and will decay, leading to fungal growth.
- You can also remove some leaves above the soil line to reduce the amount of water lost through transpiration.
Rooting Methods: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Unleash The Potential Of Your Rose Garden
Rose cuttings, once prepared, are ready for the crucial step of rooting, where they develop new roots and begin their journey into independent plant life. Several methods exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages, allowing you to choose the best approach based on your resources and preferences.
The most common methods include water propagation, soil propagation, and the use of rooting hormones. Each method offers unique advantages and disadvantages, impacting the success rate, speed of root development, and overall ease of propagation.
Comparison of Rooting Methods
Understanding the differences between these methods is crucial for selecting the most effective approach for your rose cuttings. The following table provides a concise comparison, highlighting the key aspects of each method:
Method |
Materials |
Steps |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Water Propagation |
Clear glass jar, water |
1. Place cuttings in a jar filled with clean water.
|
Simple, low-cost, allows for easy observation of root growth. |
Slower root development compared to soil propagation, higher risk of fungal infections. |
Soil Propagation |
Potting mix, rooting hormone (optional), pot |
1. Fill a pot with potting mix.
|
Faster root development, higher success rate compared to water propagation. |
Requires more effort and attention, less visual monitoring of root development. |
Rooting Hormones |
Rooting hormone powder or liquid |
1. Dip the base of the cutting in rooting hormone.
|
Significantly enhances root development, increases success rate. |
Requires additional cost, potential for over-application leading to damage. |
Nurturing Your Rose Cuttings

Once you’ve prepared your rose cuttings and chosen your rooting method, it’s time to provide them with the ideal environment for success. Creating the right conditions for rooting is crucial for your cuttings to develop strong roots and thrive.
Providing the Ideal Environment
The environment plays a crucial role in the success of your rose cuttings. Creating a conducive environment will encourage root development and promote healthy growth.
- Humidity:High humidity is essential for rose cuttings to retain moisture and prevent dehydration. A humidity dome or plastic wrap can be used to create a humid environment around the cuttings. You can also mist the cuttings regularly to maintain adequate humidity levels.
- Light:While rose cuttings need light for photosynthesis, they should be protected from direct sunlight, which can scorch the delicate leaves. Bright, indirect light is ideal for promoting healthy growth without causing damage. A south-facing window with a sheer curtain can provide the right amount of light.
- Temperature:Rose cuttings root best in warm temperatures, typically between 70-75°F (21-24°C). A warm, sunny location is ideal for rooting, but avoid placing cuttings in direct sunlight. A heated propagation mat can also be used to maintain the optimal temperature.
Caring for Cuttings During Rooting
Consistent care is vital during the rooting phase. This includes providing the right amount of moisture, light, and air circulation.
Unlocking the magic of rose propagation from cuttings is a rewarding journey for any gardener. This technique allows you to multiply your favorite rose varieties and expand your garden’s beauty. Transforming simple cuttings into stunning roses is a process that can be mastered with a few key steps, as detailed in our comprehensive guide, How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Transform Simple Cuttings into Stunning Roses.
By following the instructions, you’ll soon be enjoying the fruits of your labor, with a flourishing rose garden bursting with vibrant blooms.
- Watering:Keep the rooting medium consistently moist, but avoid overwatering. Check the moisture level by touching the soil. If it feels dry, water thoroughly. Allow excess water to drain to prevent root rot.
- Ventilation:Good air circulation is essential for preventing fungal diseases and promoting healthy root growth. If using a humidity dome or plastic wrap, remove it for a few hours each day to allow air circulation. This also helps to prevent condensation, which can lead to mold growth.
- Fertilizing:Rose cuttings do not require fertilization during the rooting phase. The focus should be on encouraging root development, not top growth. Once the cuttings have established roots and new growth appears, you can start fertilizing with a balanced fertilizer diluted to half strength.
Transplanting and Establishing Your New Roses
The moment has arrived to transfer your patiently nurtured rose cuttings from their rooting environment to their permanent homes, whether in pots or your garden. This transition requires careful handling to ensure the delicate roots establish themselves successfully.
Choosing the Right Location and Soil Conditions
The success of your new rose plants depends heavily on the location and soil conditions. Roses thrive in sunny spots receiving at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. They prefer well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter.
- Before planting, amend the soil with compost or aged manure to improve its structure and fertility.
- Test the soil pH, as roses prefer a slightly acidic to neutral range (6.0-7.0). Adjust the pH if necessary with lime or sulfur.
Transplanting Your Rooted Cuttings
Once your rose cuttings have developed a healthy root system, they are ready for transplanting.
- Prepare the Planting Hole:Dig a hole twice as wide and as deep as the root ball of your rose cutting. This allows for ample space for root expansion.
- Loosen the Roots:Gently loosen the roots of the cutting to encourage outward growth. Avoid disturbing the root ball too much.
- Position the Cutting:Place the cutting in the hole, ensuring the bud union (the point where the rootstock meets the scion) is at or slightly above soil level.
- Backfill the Hole:Carefully fill the hole with the amended soil, gently firming it around the roots to eliminate air pockets.
- Water Thoroughly:Water the newly planted rose deeply to settle the soil and provide moisture for root establishment.
Watering, Fertilizing, and Protecting Newly Planted Roses
Newly planted roses require consistent watering, especially during the first few weeks.
- Water deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings.
- Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
Fertilizing is crucial for providing essential nutrients for healthy growth.
- Apply a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for roses, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Fertilize regularly throughout the growing season, particularly during the spring and summer months.
Protecting your new roses from pests and diseases is essential for their well-being.
Unlocking the secrets of rose propagation from cuttings allows you to expand your garden with beautiful, thriving blooms. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, the process of growing roses from cuttings is surprisingly simple and rewarding.
For expert tips on how to ensure your rose cuttings thrive and produce gorgeous plants, check out this comprehensive guide: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Tips for Thriving, Gorgeous Plants. By mastering the art of rose propagation, you can create a vibrant rose garden that’s bursting with color and fragrance, all while enjoying the satisfaction of nurturing your own roses from scratch.
- Inspect your plants regularly for signs of infestation or disease.
- Use organic pest control methods or insecticidal soap to address pest problems.
- Treat fungal diseases with fungicides if necessary.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While rose propagation is generally straightforward, you might encounter some hiccups along the way. Identifying and addressing these issues promptly can significantly improve your success rate. This section explores common problems and their solutions, empowering you to overcome any obstacles and achieve a thriving rose garden.
Common Problems and Solutions
Understanding the root causes of issues is crucial for effective troubleshooting. The following table Artikels common problems encountered during rose propagation, their probable causes, and recommended solutions:
Problem |
Cause |
Solution |
|---|---|---|
Wilting Cuttings |
Dehydration, improper rooting medium, excessive heat, or fungal infection. |
Ensure adequate moisture in the rooting medium. Use a well-draining mix. Avoid direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Treat fungal infections with a fungicide. |
Fungal Diseases |
Damp, humid conditions, poor air circulation, or contaminated rooting medium. |
Maintain good ventilation. Use a sterile rooting medium. Avoid overwatering. Treat with a fungicide. |
Pest Infestations |
Insects, mites, or other pests attracted to the cuttings. |
Inspect cuttings regularly. Use insecticidal soap or neem oil to control pests. |
Slow Rooting |
Improper rooting hormones, unfavorable environmental conditions, or unsuitable cutting selection. |
Use high-quality rooting hormone. Maintain ideal temperature and humidity. Choose healthy, vigorous cuttings. |
Addressing Wilting
Wilting cuttings are a common concern, often resulting from dehydration or environmental stress. The first step is to assess the moisture level of the rooting medium. If it feels dry, water it thoroughly, ensuring the entire medium is moistened. If the problem persists, consider these factors:
- Excessive Heat:Direct sunlight or high temperatures can quickly dehydrate cuttings. Relocate them to a shaded area or adjust the temperature to a cooler range.
- Improper Rooting Medium:A dense or poorly draining rooting medium can hinder water absorption, leading to wilting. Use a well-draining mix, such as a combination of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite.
- Fungal Infections:Fungal diseases can weaken cuttings and cause wilting. Inspect for signs of fungal growth, such as mold or discoloration. If fungal infection is suspected, treat the cuttings with a fungicide.
Managing Fungal Diseases
Fungal diseases can significantly impact the success of rose propagation. Preventing fungal infections is key, and maintaining proper hygiene is essential.
- Sterile Rooting Medium:Using a sterilized rooting medium minimizes the risk of introducing fungal spores.
- Good Ventilation:Adequate air circulation helps prevent excessive moisture buildup, which can create a favorable environment for fungal growth.
- Avoid Overwatering:Allow the rooting medium to dry slightly between waterings to prevent excessive moisture.
- Fungicide Treatment:If fungal infections occur, treat the cuttings with a fungicide specifically designed for rose plants.
Controlling Pest Infestations
Pests can damage cuttings, hindering their growth and potentially spreading diseases. Regular inspection is crucial for early detection.
- Visual Inspection:Thoroughly examine the cuttings for signs of insect activity, such as holes in leaves, webbing, or sticky residue.
- Insecticidal Soap:Use insecticidal soap to control aphids, mealybugs, and other soft-bodied insects.
- Neem Oil:Neem oil is a natural insecticide that can be effective against a range of pests.
Rose Propagation: A Journey of Beauty
Rose propagation is a rewarding experience that allows you to expand your rose garden and share the beauty of these magnificent flowers with others. It’s a journey that transforms a simple cutting into a thriving rose plant, a testament to the resilience and potential of nature.
Visualizing the Propagation Process
Imagine a single rose cutting, carefully prepared and placed in a rooting medium. The cutting, devoid of roots, starts its transformation. Over time, tiny white roots emerge from the base of the cutting, anchoring it to the soil and drawing nourishment.
These roots grow stronger and more numerous, forming a network that sustains the plant. As the roots develop, the cutting begins to sprout new leaves, signaling the start of its above-ground growth. The leaves expand, gaining strength and color, showcasing the plant’s resilience and vitality.
Soon, a single stem emerges, reaching for the sun, followed by more stems, creating a lush and vibrant bush. This is the journey of a rose cutting, from a simple stem to a flourishing rose plant.
Stages of Rose Growth
The transformation of a rose cutting into a mature rose plant is a fascinating process that unfolds in distinct stages:
- Cutting Preparation:This stage involves selecting a healthy cutting from a mature rose plant, removing the leaves from the lower portion, and treating the cut end with rooting hormone. This sets the stage for root development.
- Root Development:Once placed in a suitable rooting medium, the cutting begins to develop roots. This process can take several weeks, depending on the variety of rose and the growing conditions.
- Leaf Emergence:As roots develop, the cutting starts to produce new leaves, signaling the plant’s growth and vitality.
- Stem Growth:With a strong root system established, the cutting begins to produce stems, which elongate and branch out, forming the structure of the rose plant.
- Bud Formation:As the plant matures, buds appear on the stems, eventually developing into beautiful rose blooms.
- Flowering:The culmination of the propagation process is the emergence of stunning rose blooms, showcasing the beauty and fragrance of the plant.
A Captivating Story of Success, How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Unleash the Potential of Your Rose Garden
One summer afternoon, while tending to my rose garden, I was struck by the sheer beauty of a particular rose variety. I decided to try propagating it, hoping to share its beauty with others. I carefully selected a cutting, prepared it according to the instructions, and placed it in a pot filled with a mixture of perlite and vermiculite.
I kept the pot in a warm, sunny location, ensuring the rooting medium remained moist. Weeks turned into months, and I anxiously checked the cutting for signs of growth. One day, I noticed a tiny green shoot emerging from the base of the cutting, a sign that roots were forming.
My heart skipped a beat with joy and excitement. Over time, the cutting transformed into a vibrant rose plant, a testament to the magic of propagation. The joy of seeing my efforts bear fruit, of creating a new life from a simple cutting, was truly rewarding.
This experience solidified my love for rose propagation and inspired me to share the joy of this process with others.
Final Conclusion
Propagating roses from cuttings is a fulfilling and rewarding experience, allowing you to cultivate your own rose paradise. With the right knowledge, patience, and care, you can successfully transform cuttings into flourishing rose bushes, adding vibrant beauty and fragrance to your garden.
So, gather your tools, select your favorite rose varieties, and embark on this captivating journey of rose propagation. Your garden will thank you for it!
FAQ Compilation
What are the best types of roses for propagation?
Hybrid tea roses, floribunda roses, and grandiflora roses are generally easy to propagate from cuttings.
Can I propagate roses from store-bought roses?
Yes, you can propagate roses from store-bought roses, but make sure they are not grafted roses. Look for roses with their own root systems.
What happens if my cuttings don’t root?
Don’t worry! Sometimes cuttings fail to root. Ensure you follow the steps carefully and try again with fresh cuttings.
How long does it take for rose cuttings to root?
Rooting time varies, but it usually takes 4 to 8 weeks for rose cuttings to develop roots.
