How to Propagate African Violets for Bigger, Healthier Plants – African violets are beloved for their delicate blooms and vibrant foliage, but these tropical beauties can be finicky. Sometimes, even with the best care, your African violet might not thrive.
But don’t despair! You can easily multiply your collection and create healthier, more robust plants by propagating them yourself. This guide will walk you through the different propagation methods, from leaf cuttings to division, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to cultivate thriving African violet plants.
Whether you’re a seasoned plant enthusiast or a novice gardener, propagating African violets is a rewarding experience. Not only does it allow you to expand your collection, but it also helps you to understand the unique needs of these plants and fosters a deeper connection with your green companions.
Let’s delve into the world of African violet propagation and unlock the secrets to growing bigger, healthier plants.
Understanding African Violet Propagation: How To Propagate African Violets For Bigger, Healthier Plants
Propagating African violets is a rewarding and relatively simple process that allows you to create new plants from existing ones. There are several methods you can use, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these methods will help you choose the best approach for your needs.
Methods of Propagation
There are three primary methods of propagating African violets: leaf cuttings, stem cuttings, and division.
- Leaf Cuttings:This is the most common and successful method of propagating African violets. It involves taking a healthy leaf from a mature plant and rooting it in a suitable medium. Leaf cuttings are easy to take and can produce multiple new plants from a single leaf.
- Stem Cuttings:This method involves taking a section of stem with a few leaves attached and rooting it in a growing medium. Stem cuttings are often used to propagate specific varieties or to preserve the characteristics of a particular plant.
- Division:This method involves separating a mature plant into multiple smaller plants. Division is typically done when the plant becomes overcrowded or when you want to create new plants from a single parent plant.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
- Leaf Cuttings:
- Advantages:High success rate, easy to implement, can produce multiple plants from a single leaf.
- Disadvantages:Slower growth compared to other methods, may take longer to flower.
- Stem Cuttings:
- Advantages:Produces plants with similar characteristics to the parent plant, faster growth than leaf cuttings.
- Disadvantages:Lower success rate than leaf cuttings, may be more difficult to root.
- Division:
- Advantages:Fastest method of propagation, produces mature plants quickly.
- Disadvantages:Requires a mature plant, can be stressful for the parent plant, not suitable for all varieties.
Comparison of Propagation Methods
Method |
Success Rate |
Time to Maturity |
Ease of Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
Leaf Cuttings |
High |
6-12 months |
Easy |
Stem Cuttings |
Moderate |
4-8 months |
Moderate |
Division |
Variable |
Immediate |
Moderate to Difficult |
Preparing for Propagation

Before embarking on the journey of propagating African violets, it’s crucial to gather the necessary tools and materials and create the ideal environment for successful rooting. This section will delve into the specific requirements for preparing for propagation, ensuring a smooth and productive process.
Essential Tools and Materials
A well-equipped toolkit is vital for propagating African violets. Here’s a list of essential tools and materials:
- Sharp, sterilized knife or scissors:For cleanly cutting leaf cuttings or stem sections.
- Rooting hormone (optional):Promotes root development and increases the success rate of propagation.
- Small pots or trays:To house the cuttings during the rooting process. Choose pots with drainage holes.
- Rooting medium:A specialized mix designed for propagation, providing adequate drainage and aeration. Common options include:
- Vermiculite:A lightweight, sterile, and airy medium, ideal for rooting.
- Perlite:Another lightweight and airy medium, providing good drainage.
- Peat moss:Holds moisture well but requires careful watering to prevent over-saturation.
- Coco coir:A natural and sustainable option, providing good drainage and aeration.
- Seed starting mix:A readily available option, typically containing a blend of peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite.
- Water:For watering the rooting medium and keeping it consistently moist.
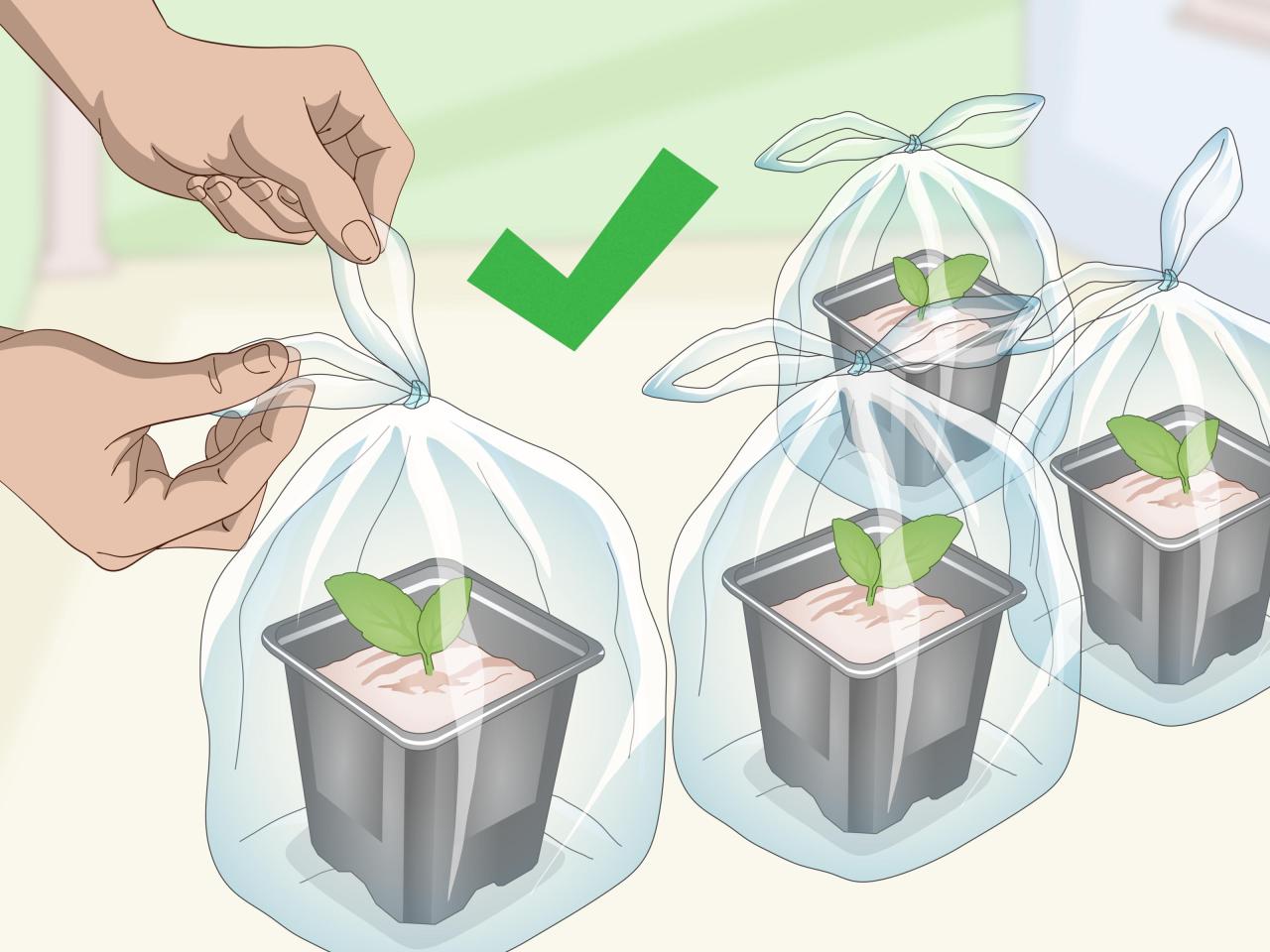
- Plastic wrap or humidity dome:To create a humid environment for the cuttings, promoting root development.
- Labels:To identify the cuttings and track their progress.
Ideal Environment for Propagation
African violet cuttings thrive in a warm, humid environment with indirect light.
- Temperature:The ideal temperature range for rooting African violet cuttings is between 70°F and 75°F (21°C to 24°C). Consistent warmth encourages root development and prevents chilling.
- Humidity:African violets prefer high humidity, which is essential for successful rooting. A humidity dome or plastic wrap helps create a humid environment, preventing the cuttings from drying out. Misting the cuttings periodically can also increase humidity levels.
- Light:Bright, indirect light is best for propagation. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the cuttings. A south-facing window with a sheer curtain or a grow light can provide adequate light.
Preparing the Rooting Medium
The rooting medium plays a crucial role in providing the necessary environment for root development.
- Choosing the right medium:Select a rooting medium that provides good drainage and aeration, while retaining moisture. Vermiculite, perlite, or a seed starting mix are common choices. Avoid using regular potting soil, as it can be too dense and hold too much moisture, leading to root rot.
- Moistening the medium:Thoroughly moisten the rooting medium before planting the cuttings. It should be damp but not soaking wet.
- Filling the pots or trays:Fill the pots or trays with the moistened rooting medium, leaving about an inch of space at the top. Gently press the medium down to create a firm base for the cuttings.
Leaf Cutting Propagation
Leaf cutting propagation is a popular and effective method for multiplying African violets. It involves taking a healthy leaf from the parent plant and encouraging it to develop roots and a new plant. This method is relatively simple and can be done by anyone with basic gardening skills.
Preparing Leaf Cuttings
Before taking a leaf cutting, it’s crucial to select a healthy, mature leaf from your African violet plant. Avoid using leaves that are damaged, diseased, or have any signs of pests. The ideal leaf for propagation should be firm, with a vibrant green color and no signs of yellowing or browning.
- Choosing the Right Leaf:Select a healthy, mature leaf from the plant, preferably from the lower part of the plant. Avoid leaves that are damaged, diseased, or have any signs of pests. The ideal leaf for propagation should be firm, with a vibrant green color and no signs of yellowing or browning.
- Trimming the Leaf:Using a sharp, clean knife or pair of scissors, make a clean cut about an inch below the leaf’s base. The cut should be angled to prevent water from collecting on the leaf’s surface.
- Removing Excess Leaves:If the leaf has multiple leaves, you can remove the smaller, underdeveloped leaves to concentrate the plant’s energy on root development. Leave at least one or two leaves on the cutting to provide energy for the plant.
Placing Leaf Cuttings in the Rooting Medium
Once you have prepared your leaf cuttings, you can place them in a rooting medium to encourage root development.
- Choosing the Rooting Medium:A mixture of equal parts perlite and vermiculite is an excellent choice for rooting African violet leaf cuttings. This mixture provides good drainage and aeration, essential for root growth.
- Preparing the Rooting Medium:Moisten the rooting medium thoroughly and fill small pots or trays with it. Make sure the medium is not too compacted.
- Inserting the Leaf Cutting:Insert the cut end of the leaf cutting into the rooting medium, making sure that at least half of the leaf is buried. The leaf blade should be exposed to light.
- Watering:Water the cuttings thoroughly, but avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot. Keep the medium consistently moist, but not soggy.
Maintaining Optimal Conditions for Root Development
Once the leaf cuttings are planted, it’s essential to provide them with the right conditions to encourage root development.
- Light:Place the cuttings in a bright, indirect light location, avoiding direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves. A south-facing window with a sheer curtain is ideal.
- Temperature:African violets thrive in warm temperatures, around 70-75°F (21-24°C). Avoid placing them in drafty areas or near cold windows.
- Humidity:African violets prefer humid environments. You can increase humidity by placing the pots on a tray filled with pebbles and water. Misting the leaves regularly can also help.
- Ventilation:Ensure good air circulation around the cuttings. Avoid overcrowding, as this can lead to fungal diseases.
Stem Cutting Propagation
Stem cutting propagation is another method for multiplying African violets, and it’s a great way to get more plants quickly. This method involves taking cuttings from the stems of your African violet, which will then root and develop into new plants.
This method is especially useful for propagating African violets with unique or desirable traits, such as specific flower colors or leaf patterns.
Preparing Stem Cuttings
Before taking stem cuttings, it’s important to select healthy stems from your African violet plant. Look for stems that are firm, have at least one node (the point where leaves grow from the stem), and are free of any diseases or pests.
Nodes are crucial for stem cuttings because they contain the plant’s growth hormones, which will encourage root development. Once you’ve selected a suitable stem, use a sharp, sterilized knife or pair of scissors to make a clean cut just below a node.
This will help prevent the stem from rotting. Then, remove the lower leaves from the stem cutting, leaving only the top few leaves intact. This will reduce the amount of energy the cutting needs to expend on maintaining leaves and direct it towards root development.
Rooting Stem Cuttings
After preparing the stem cuttings, you’ll need to prepare a rooting medium. A suitable rooting medium should be well-draining and moisture-retentive. Popular choices include a mix of perlite and vermiculite, peat moss, or a commercial rooting mix. To root the stem cuttings, you can use a variety of methods:
- Water Propagation:Place the stem cutting in a glass of water, ensuring the node is submerged. Change the water every few days to prevent bacteria growth. This method is simple but can be slow.
- Rooting Hormone:Dip the cut end of the stem cutting in a rooting hormone powder or solution. This helps stimulate root growth.
- Rooting Tray:Fill a rooting tray with the prepared rooting medium. Make small holes in the medium and insert the stem cuttings. Water the tray thoroughly and place it in a warm, bright location out of direct sunlight.
Stem cuttings typically take a few weeks to root. Keep the rooting medium moist but not soggy, and ensure the cuttings are in a warm, humid environment. Once the cuttings have rooted, they can be transplanted into individual pots filled with African violet potting mix.
Division Propagation
Division propagation is a simple and effective method for multiplying your African violet collection. It involves separating an established plant into multiple divisions, each with its own roots and leaves, and repotting them individually. This technique is ideal for rejuvenating overcrowded plants and creating new, healthy plants.
Dividing an Established Plant
When an African violet plant becomes overcrowded, it can benefit from division. This process involves carefully separating the plant into multiple divisions, each with its own root system and leaves. To divide an established plant, follow these steps:
- Choose the right time:The best time to divide an African violet is during the spring or early summer when the plant is actively growing.
- Prepare the plant:Gently remove the plant from its pot, being careful not to damage the roots. Shake off any excess soil and loosen the root ball slightly.
- Separate the divisions:Look for natural divisions in the plant, where the root ball appears to be naturally splitting. Use your fingers or a sharp, clean knife to gently separate the divisions. Ensure each division has a healthy root system and at least a few leaves.
- Inspect the divisions:After separating the divisions, inspect the roots and leaves for any signs of damage or disease. Remove any damaged or diseased parts with a clean, sharp knife.
Repotting the Divisions, How to Propagate African Violets for Bigger, Healthier Plants
Once the divisions are separated, you can repot them in individual pots. The pot size should be appropriate for the size of the division, allowing room for the roots to grow. Here are some tips for repotting the divisions:
- Choose the right potting mix:Use a well-draining potting mix specifically formulated for African violets. Avoid using heavy soils that can retain too much moisture.
- Fill the pot:Fill the pot with potting mix, leaving about an inch of space at the top.
- Plant the division:Place the division in the center of the pot, ensuring the crown (where the leaves meet the roots) is at or slightly above the soil level.
- Backfill with soil:Gently fill in the pot with potting mix, leaving a small space around the base of the division.
- Water thoroughly:Water the division thoroughly after repotting to settle the soil and ensure the roots are well hydrated.
Providing Care for Healthy Growth
After repotting, provide the new divisions with the same care as established African violets:
- Bright, indirect light:African violets thrive in bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
- Consistent moisture:Water the divisions when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
- Fertilize regularly:Fertilize the divisions with a balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength every two weeks during the growing season.
- Maintain humidity:African violets prefer humid environments. You can increase humidity by placing the pots on a pebble tray filled with water or by using a humidifier.
Care and Maintenance
After successfully propagating your African violets, providing proper care and maintenance is crucial for their continued growth and health. These newly rooted plants require specific conditions to thrive and develop into robust, flowering plants.
Optimal Care and Maintenance Practices
A well-structured care regimen is essential for newly propagated African violets. This table summarizes the optimal practices for ensuring their healthy growth and development.| Care Practice | Description | Importance ||—|—|—|| Watering| Water thoroughly when the top inch of soil is dry.
Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot. | Consistent moisture without saturation promotes healthy root development and prevents fungal infections. || Fertilization| Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer diluted to half strength every two weeks during the growing season.
| Provides essential nutrients for vigorous growth and abundant flowering. || Light Exposure| Place the plants in bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves. | Adequate light encourages photosynthesis and healthy leaf development. || Temperature| Maintain a temperature between 65°F and 75°F (18°C and 24°C).
| African violets thrive in warm environments, promoting optimal growth and flowering. || Humidity| Provide moderate humidity, around 40-50%. | High humidity prevents leaf dehydration and promotes healthy leaf growth. || Repotting| Repot the plants into slightly larger pots when they become root-bound.
| Provides adequate space for root growth and prevents stunted development. |
Signs of Healthy Growth
Healthy African violets exhibit several characteristics that indicate their well-being. These signs include:
Vibrant, green leaves
Healthy leaves are a key indicator of overall plant health. They should be firm, plump, and free from any discoloration or damage.
New growth
The presence of new leaves and stems indicates that the plant is actively growing and thriving.
Abundant flowering
African violets are known for their prolific flowering. A healthy plant will produce numerous blooms, adding to its beauty and appeal.
Common Problems During Propagation
While propagation is generally successful, some common problems may arise during the process. Recognizing these issues early can help prevent further complications and ensure the healthy development of your new plants.
Root Rot
Overwatering is a common cause of root rot. This fungal disease can damage or destroy roots, leading to wilting and plant death.
Leaf Spotting
Leaf spotting can be caused by various factors, including fungal infections, bacterial diseases, and pests. It can result in unsightly blemishes on the leaves.
Stunted Growth
Inadequate light, nutrient deficiencies, or root-bound conditions can lead to stunted growth, resulting in smaller, weaker plants.
Promoting Bigger, Healthier Plants
After successfully propagating your African violets, you’ll want to nurture them to reach their full potential. This section will guide you through the steps to promote bigger, healthier plants, ensuring they thrive and produce beautiful blooms.
Repotting for Growth
Repotting is crucial as your African violets grow, providing them with the space they need to develop a robust root system and flourish.
- Choose the Right Potting Mix:African violets prefer a well-draining, slightly acidic potting mix. A mix specifically designed for African violets or a combination of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite is ideal. Avoid heavy clay-based mixes that can retain too much moisture.
- Select the Appropriate Container Size:As your African violet grows, you’ll need to repot it into a slightly larger container. Opt for a pot that is only 1-2 inches wider in diameter than the previous one. Too large a pot can lead to excessive moisture retention and root rot.
- Repotting Process:Gently remove the plant from its current pot, being careful not to damage the roots. Loosen any tightly packed roots and inspect for any signs of disease or rot. Place the plant in the new pot, ensuring the crown (where the leaves meet the stem) is slightly above the soil line.
Fill the pot with the potting mix, leaving about an inch of space at the top. Water thoroughly after repotting.
Fertilization for Healthy Growth
Fertilizing your African violets provides them with the essential nutrients they need to grow vigorously and produce abundant blooms.
- Choose a Balanced Fertilizer:Opt for a balanced fertilizer specifically designed for African violets or other flowering plants. A balanced fertilizer has equal amounts of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), which are crucial for healthy growth, flowering, and root development.
- Fertilize Regularly:Fertilize your African violets every 2-4 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer). Avoid over-fertilizing, as it can damage the roots and lead to nutrient imbalances.
- Dilute the Fertilizer:Always dilute the fertilizer according to the manufacturer’s instructions. A weaker solution is better than a strong one. Using too much fertilizer can burn the roots and cause leaf discoloration.
Light Exposure for Optimal Growth
Light is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Providing your African violets with the right amount of light is crucial for their healthy growth and flowering.
- Bright, Indirect Light:African violets thrive in bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch their leaves. A south-facing window with a sheer curtain or a north-facing window with bright indirect light is ideal.
- Avoid Drafts and Temperature Fluctuations:African violets prefer stable temperatures and humidity. Avoid placing them near drafty windows or heat sources, as this can stress the plants and hinder their growth.
Closing Notes

Propagating African violets is a rewarding journey that allows you to create a flourishing collection of these beautiful plants. By mastering the techniques of leaf cuttings, stem cuttings, and division, you can ensure the health and longevity of your African violets.
Remember, with patience and a touch of care, you can transform a single plant into a thriving community of vibrant blooms. So, gather your tools, prepare your rooting medium, and embark on this exciting adventure of propagation, nurturing your African violets to their fullest potential.
FAQs
What is the best time of year to propagate African violets?
Spring and summer are generally considered the best times to propagate African violets, as they provide warmer temperatures and longer days, which are ideal for root development.
How do I know if my African violet cuttings are rooting?
You can check for root development by gently tugging on the cutting. If it offers resistance, roots are likely forming. You may also notice small, white roots emerging from the base of the cutting.
What should I do if my African violet cuttings are not rooting?
If your cuttings are not rooting, ensure you are providing optimal conditions, such as warm temperatures, adequate humidity, and indirect light. You can also try using a rooting hormone to encourage root development.
How often should I water my newly propagated African violets?
Water your newly propagated African violets when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot.
How long does it take for African violet cuttings to produce flowers?
It can take anywhere from 6 to 12 months for African violet cuttings to produce flowers, depending on the variety and growing conditions.
